Supersonic Sparrow III Missile
Introduction
The Sparrow II missile is an air-to-air missile developed by Raytheon in the 1950s. The vortices generated by the thin and long fuselage interfere with the missile fins, making accurate aerodynamic performance prediction difficult. We performed simulations at various angles of attack and compared the aerodynamic coefficients with wind tunnel experiments and other CFD results.

Conditions
- Compressible steady flow
- Mach No. = 1.5
- Static Pressure = 18114.8 Pa
- Static Temperature = 233.793 K
- Reynolds No. = 8.20E06
- Angle of Attack = 0, 5, 11, 17, 23, 27, 32 deg
- Reference length = 0.5486 m
- Reference area = 7.30E-04 m^2
FAMUS Setup
- Number of points of octree is about 2.5 million
- Number of points of boundary layer is about 2.7 million
- Viscosity model : SST k-omega turbulence model
- Discretization = 3rd order MLP
- Time marching = LU-SGS
- Flux scheme = M-AUSMPW+
Simulation Result
- Pressure contour(AOA=11)
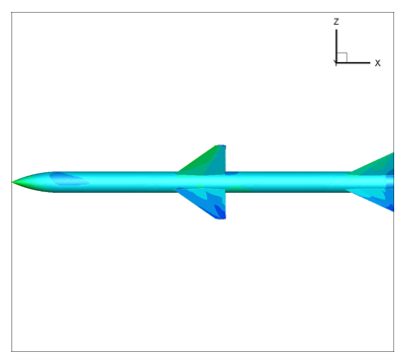
- Pressure coefficient
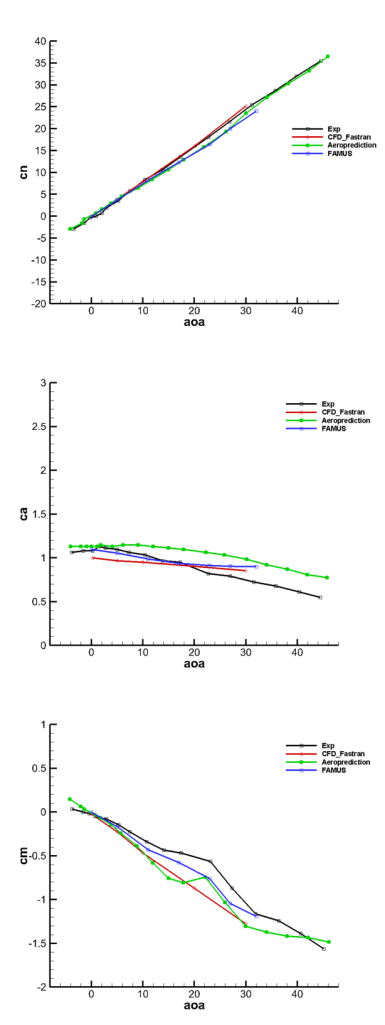
References
- Monta, W. J. Supersonic aerodynamic characteristics of a sparrow iii type missile model with wing controls and comparison with existing tail-control results. NASA, Scientific and Technical Information Office, 1997.
- Atik, H., et al. Prediction capabilities and comparison of panel, semi-empiric and cfd codes for missile aerodynamic analysis. AIAA conference, 2008.
